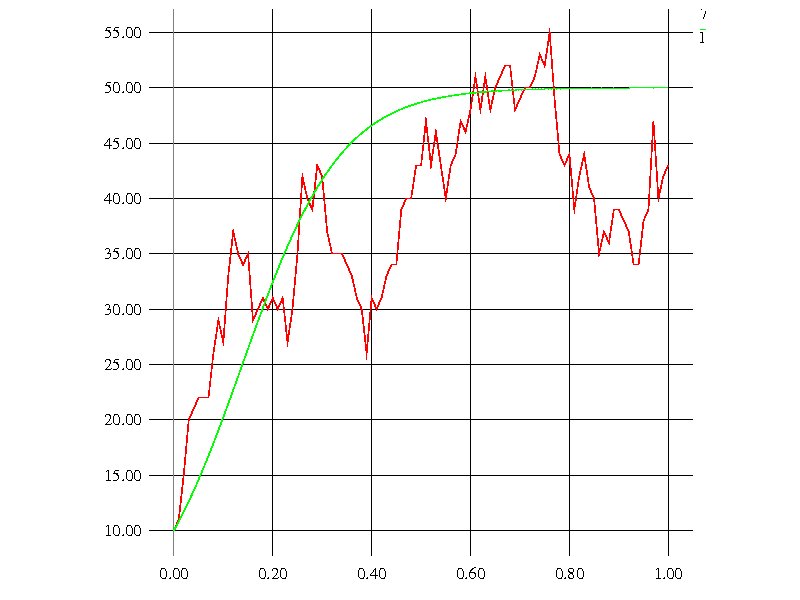
/* Individual Based Model RULE: An event A that occurs with probability P is equivalent to 1) Generate a random number X that distributes uniformly between 0 and 1. 2) If X < P, we assume the event A has occured. Otherwise, the event A did not occur. ********************************** Logistic growth model dN/dt=r(1-N/K)N We here assume that birth(N) is the probability that an individual gives birth to a new offspring per unit time and that death(N) is the probability that this individual dies. That is, for all individuals, 1) reproduction of a new individual occurs with probability birth(N)’t, or 2) death occurs with probability death(N)’t, or 3) nothing happens with probability 1 - birth(N)’t - death(N)’t where ’t is a time interval. These three events are assumed to occur mutually exclusively. Then the algorithm would be For all individuals repeat 1) Give birth to a new individual with probability birth(N)’t. 2) Remove this individual with probability death(N)’t. */ #include#include #include #define b1 0.2 #define b2 0.002 #define d1 0.1 #define d2 0.0 #define INTV 10 #define DT 0.1 /*h ͺ*/ #define IM1 2147483563 #define IM2 2147483399 #define AM (1.0/IM1) #define IMM1 (IM1-1) #define IA1 40014 #define IA2 40692 #define IQ1 53668 #define IQ2 52774 #define IR1 12211 #define IR2 3791 #define NTAB 32 #define NDIV (1+IMM1/NTAB) #define EPS 1.2e-7 #define RNMX (1.0-EPS) double birth_rate(int n); double death_rate(int n); double ran2(); unsigned long int idum =1024; main() { int pop_size, new_indiv, dead_indiv; /*population size*/ int i,step; /*j;step number*/ double prob1,prob2, ran; /*for probabilities*/ pop_size=10; /*initial population size*/ for(step=0;step<=1000;step++) { if(step % INTV==0) printf("%d %d\n",step, pop_size); new_indiv=0; dead_indiv=0; prob1=birth_rate(pop_size)*DT; prob2=death_rate(pop_size)*DT; for(i=1;i<=pop_size;i++) { ran = ran2(&idum); if (ran < prob1) new_indiv++; else if (prob1 < ran && ran < prob1 + prob2) dead_indiv++; if (pop_size < 0) pop_size = 0; /*pop.size cannot be negative */ } pop_size+=(new_indiv-dead_indiv); } return 0; } double birth_rate(int n) { double tmp; tmp=b1-b2*(double)n; return tmp; } double death_rate(int n) { double tmp; tmp=d1+d2*(double)n; return tmp; } double ran2(long *idum) { int j; long k; static long idum2=123456789; static long iy=0; static long iv[NTAB]; float temp; if(*idum <= 0){ if(-(*idum) < 1) *idum=1; else *idum = -(*idum); idum2=(*idum); for(j=NTAB+7; j>=0; j--){ k=(*idum)/IQ1; *idum=IA1*(*idum-k*IQ1)-k*IR1; if(*idum < 0) *idum += IM1; if(j < NTAB) iv[j] = *idum; } iy=iv[0]; } k=(*idum)/IQ1; *idum=IA1*(*idum-k*IQ1)-k*IR1; if(*idum < 0) *idum += IM1; k=idum2/IQ2; idum2=IA2*(idum2-k*IQ2)-k*IR2; if(idum2 < 0) idum2 += IM2; j=iy/NDIV; iy=iv[j]-idum2; iv[j]=*idum; if(iy<1) iy += IMM1; if((temp = AM*iy) > RNMX) return RNMX; else return temp; }
oΝΚ
Back to C Language